
The contemporary categories, based on formal criteria and however named, are more numerous than the traditional parts of speech and can be subcategorized. Some contemporary linguists and grammarians prefer to avoid the traditional term others use it by and large in the same sense as word class, and treat the two as interchangeable. This mixture has posed problems for 20c grammarians, and since the development of structural LINGUISTICS, many have come to prefer the term WORD CLASS, for which the criteria are rigorously restricted to form alone. The parts of speech are traditionally defined by a mixture of formal and notional criteria. Traditional grammars of English generally list eight parts of speech: NOUN, PRONOUN, VERB, ADJECTIVE, ADVERB, PREPOSITION, CONJUNCTION, INTERJECTION. A GRAMMATICAL CATEGORY or class of words. English examples include the negative ‘not’ and the polite ‘ please’.PART OF SPEECH. Similarly fast is an adjective in the sequence ‘a fast car’ but an adverb in the sentence ‘He drove fast’.Ī few words exhibit behavior that cannot be assigned to any part of speech at all. For example, book is a noun in the sentence ‘Give me that book’ but a verb in the sentence ‘Book your tickets early’.

In English, it is possible to assign a single word to two or more parts of speech. Words placed together in a single part of speech have important grammatical properties in common, but that doesn’t mean that all the words in a single part of speech have grammatical properties which are entirely identical. For example, words are classified according to the positions in which they can occur in a sentence and the way they change their forms for grammatical reasons. Words are assigned to parts of speech according to their grammatical behavior.

For example, determiners and degree modifiers are also sometimes considered as different parts of speech. Some dictionaries recognize more than eight parts of speech.
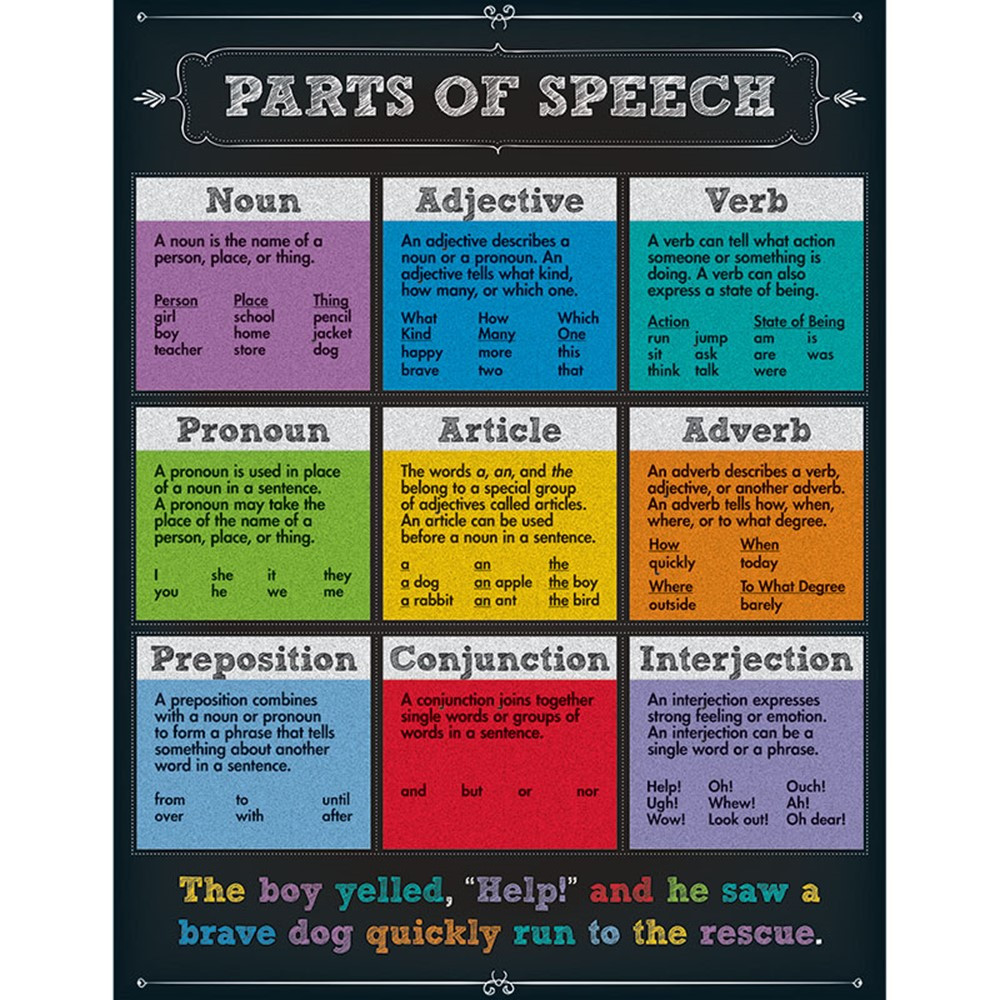
English, for example has eight parts of speech: noun, pronoun, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, verb and interjection. Languages differ in the parts of speech they have. These different classes of words are called the parts of speech. On the basis of their grammatical behavior the words of a language are divided into several classes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
